
Smart Rehab
Smart Rehab: Innovative devices based on Advanced Materials (ElectroRheological Fluids) for lower limb rehabilitation applications
(December 2019 / September 2023)
- Programme: POR FESR Sicilia 2014-2020 Azione 1.1.5
- Coordinator: Signo Motus
- Consortium: 8 partners (IT)
- Website: www.smartrehab.it
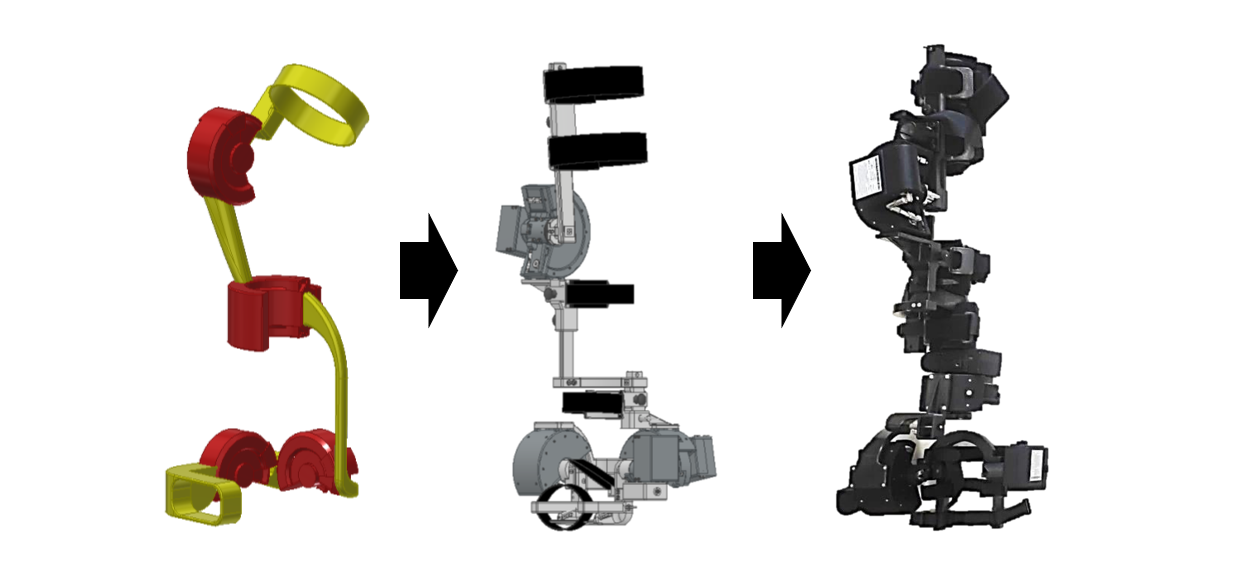
Abstract
The project involves the development, validation in a laboratory environment (TRL4), in a relevant environment (TRL5) and demonstration in a relevant environment (TRL6) of low-cost wearable semi-active rehabilitation robotic devices based on Advanced Materials (ElectroRheological Fluids) aimed at optimizing and personalizing rehabilitation treatment for the lower limb. The modular devices are worn by the patient, enabling the execution of rehabilitation exercises in a virtual environment in reference to a specific personalized target in relation to the planned rehabilitation path. The device, during the execution of the movement, can be programmed to generate variable resistance in relation to the patient's position and intention of movement. This customization is selective with respect to the different muscular districts of each joint of the lower limb (knee and ankle), enabling motor training in patients with post-trauma (orthopaedic) or stroke (neurological) outcomes, increasing their muscle tone and functional recovery. The device is able, for example, to simulate the effect of a rehabilitation treatment in water by making the patient interact with a variable viscous resistance. The integration with virtual reality/augmented reality (VR/AR) systems also allows the involvement of the patient by immersing him in virtual scenarios, increasing the adherence and effectiveness of the rehabilitation treatment through "rewarding" mechanisms and personalized feedback based on the completion of the exercises and the results achieved. The modular wearable device features a kinematic chain compatible with the patient's anatomical chain (1 or 2 degrees of freedom for knee joint rehabilitation and 2 or 3 degrees of freedom for ankle rehabilitation). The specific configuration of the joints and the presence of adjustable links allows for high adaptability to the different anthropometric parameters of the patients and to simplify the donning and removal procedures.
The system, equipped with a controller and a power module (battery/power supply), is connected to a remote device (PC or smartphone) via a wireless communication channel (WiFi/Bluetooth). A software application is used for: controlling the device; exercise programming; data acquisition; checking the results against the expected target. Professionals have an environment available to set up rehabilitation sessions and evaluate the progress achieved by each patient. Different rehabilitation protocols and related exercises can be configured in order to achieve specific clinical targets in relation to the needs of the patients. In particular, these devices will be tested in:
- orthopedic rehabilitation: post-operative functional recovery for hip, knee and ankle prostheses (with evaluation of the possible use at the patient's home, benefiting from the low cost of the devices);
- neurological rehabilitation (e.g. cerebral stroke): early verticalization of patients with stroke outcomes and recovery of walking.
- definition of the functional requirements and technical specifications of the devices through the contribution of reference clinical centers (PHASE I)
- research and development activities on ER Fluids with the dual objective of maintaining a high technological level (improvement of current performance) and optimizing production processes (from laboratory to industry) (PHASE II);
- device design with preliminary experimental verification regarding key points such as usability, work space, wearability (PHASE III);
- manufacturing (alpha release) of the devices and validation in the laboratory (TRL4) with subsequent upgrade (beta release) and validation in the relevant environment (TRL5) (PHASE IV);
- development of a virtual reality system with serious games to interface with the devices to create a playful environment during the execution of the rehabilitation treatment (PHASE V);
- realization (final release) of the devices and demonstration in a relevant environment (TRL6) through a suitable clinical trial (PHASE VI).
In conclusion, within the project, it is expected the development, prototyping and demonstration in a relevant environment (TRL 6) of low-cost modular wearable semi-active devices for the rehabilitation of the lower limb composed of one device for knee (1 or 2 DOF) and one for ankle (2 or 3 DOF).



